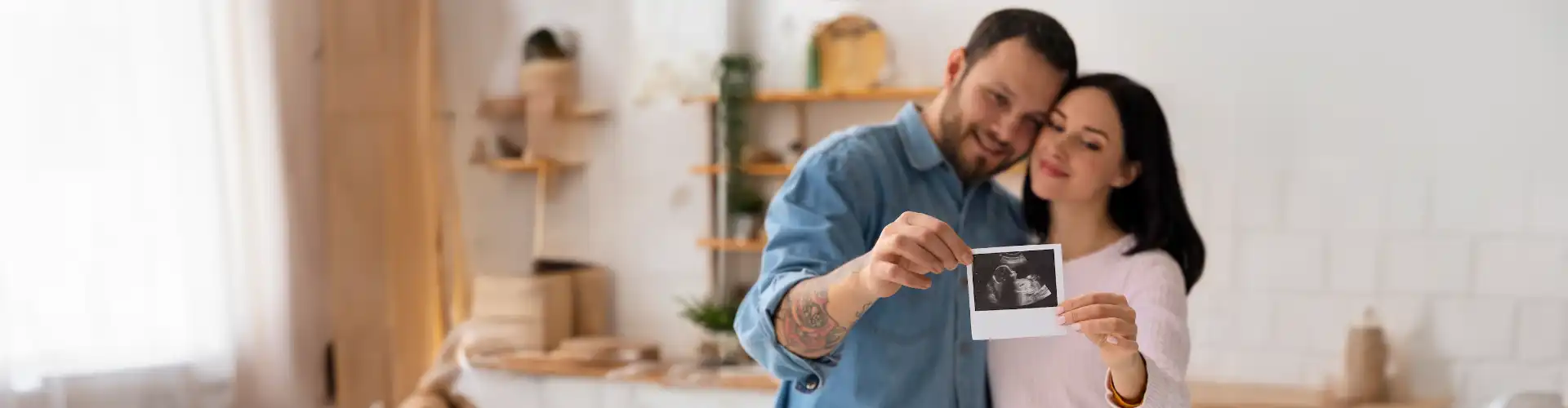

Surrogacy is a reproductive arrangement in which a woman, known as the surrogate, carries and delivers a child for another person or couple known as the intended parents. There are two types of surrogacy: traditional and gestational. In traditional surrogacy, the surrogate becomes genetically linked to the child when her own egg is fertilized, often by the intended father's sperm. The more prevalent method, gestational surrogacy, involves the implantation of an embryo developed by in vitro fertilization (IVF) into the surrogate's uterus.
In this situation, the surrogate has no genetic ties to the child. Surrogacy is a possible alternative for persons experiencing fertility issues, medical disorders that prevent pregnancy, or same-sex couples. It is a complicated process including legal agreements, medical procedures, and fertility clinic participation, with rules and regulations varied greatly between jurisdictions.
Surrogacy allows individuals or couples who are unable to conceive due to medical reasons to have a biological connection to their kid through the use of their own eggs and sperm or donor gametes.
Surrogacy provides a road to motherhood for same-sex couples by allowing them to have a genetically related child with the help of a surrogate and assisted reproductive technology.

Women who are unable to bear a pregnancy due to physical reasons such as a weaker uterus or a history of miscarriage can nonetheless become biological parents through surrogacy.

Intended parents can be involved in the pregnancy experience, from surrogate selection to prenatal care and birthing, giving them a sense of control and connection to the process.
Both the intended parents and the surrogate get complete medical exams to check their overall health and reproductive fitness. The surrogate's health is closely examined, with an emphasis on the condition of her uterus and the absence of any potential pregnancy hazards.
If the intended mother contributes her eggs, she undergoes ovarian stimulation with hormonal medicines in order to produce numerous eggs. Following egg harvesting, which is normally accomplished through a simple surgical operation, embryos are created using in vitro fertilization (IVF).
Following embryo production, a thorough selection process is carried out to determine the most viable embryos for transfer. Preimplantation genetic testing (PGT) may be used by intended parents to screen for genetic disorders.
Medications are used to synchronize the surrogate's menstrual cycle with that of the intended mother or egg donor. This synchronization increases the likelihood of a successful embryo transfer.
In a brief outpatient procedure, the selected embryos are tenderly transferred to the surrogate's uterus. The surrogate rests after the transfer to increase the chances of successful embryo implantation.
Once the pregnancy is confirmed, the surrogate is subjected to regular medical check-ups to track the pregnancy's progress. To keep involved with the process, intended parents actively participate in critical medical appointments and ultrasounds.
The surrogate gives birth, frequently in the presence of the intended parents. Following births, legal proceedings are undertaken to establish the legal paternity of the intended parents, ensuring a smooth transition of custody.
Couples who are unable to conceive owing to medical reasons, such as uterine problems, repeated pregnancy loss, or other fertility disorders, may consider surrogacy to satisfy their desire for motherhood.
Surrogacy provides a road to motherhood for same-sex couples in situations where both parties are unable to carry a child. A gestational surrogate might be used in such instances to carry the pregnancy.
Surrogacy may be used by individuals or couples who have medical issues that make pregnancy dangerous or difficult. Women with cardiac disorders, severe diabetes, or other health issues that pose a danger during pregnancy may be included.
Women who have had a hysterectomy or who have congenital uterine defects may need the help of a gestational surrogate to bear a pregnancy.
Couples who have had multiple miscarriages or pregnancy losses may consider surrogacy to boost their chances of having a successful pregnancy and childbirth.
Starting the search for a surrogate carrier is a comprehensive process. Intended parents usually start by studying and educating themselves on the legal and ethical aspects of surrogacy, which is followed by a critical decision on whether to engage with a surrogacy agency or seek an independent arrangement. The screening and matching step, which is assisted by the chosen route, evaluates the compatibility of intended parents and surrogates based on a variety of parameters.
Following that, legal discussions are held in order to draft thorough agreements describing rights, obligations, and expectations. The next steps are medical assessments, fertility treatments, and embryo transfers, with continued emotional support for all parties throughout the pregnancy. Finally, legal procedures are carried out to establish parental rights, culminating in the wonderful occasion of the child's birth. Throughout this complicated process, compassion, clear communication, and legal counsel are critical to achieving a successful and respectful surrogacy experience.

Aarti Hospital 2026. All rights reserved.